DROUGHT
Drought is a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall leading to a water shortage. There are four phases of drought: meteorological, agricultural, hydrologic, and socioeconomic. There is a lag between meteorological and hydrological factors. Utah is the second driest states in the US with an average of 13 inches of precipitation annually. The state’s watersheds and aquifers are refilled by snowmelt. Drought is impacted by natural factors including winter precipitation, soil saturation, temperatures and man-made factors like population growth, water demand, and water storage.
Residential and commercial development is concentrated on agricultural land pushing out livestock grazing land and crop fields. Low reservoirs affect irrigation and culinary water supplies, agriculture and agribusinesses, ecosystems, plant species, wildlife mortality rates and migration patterns, and heightens the risk of wildfire.
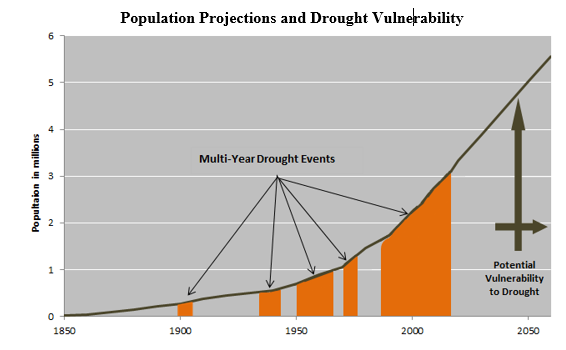
The Palmer Drought Severity Index developed in the 1960’s measures levels of dryness and wetness compared to historic norms. There are seven climate divisions in Utah, Western, Dixie, North Central, South Central, Northern Mountains, Uinta Basin, and Southeast. Drought occurs when there are persistent below average precipitation levels across all of Utah’s seven climate divisions during the same time period. In Utah there have been six statewide multi-year drought periods from 1895 to 2017 and four multi-year wet periods.
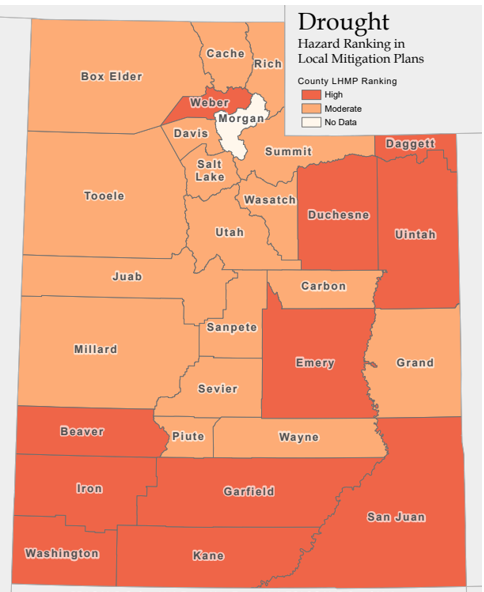
In 2018 Governor Herbert declared a State of Emergency due to statewide drought conditions and six individual Utah counties declared drought-related disasters: Box Elder, Carbon, Grand, Emery, San Juan, and Wayne. The effects of drought persist for years after normal precipitation levels return. The Division of Water Resources (DWRe) emphasizes limited water availability and a growing population make Utah more vulnerable to environmental, agricultural, economical and societal stresses resulting from drought. The DWRe advocates innovative water management strategies to sustain the water needs of Utah’s population. Proposed solutions include: water redistribution, conjunctive management, water systems interconnections, water development projects, water reuse, demand management (alternative landscaping and incentive pricing) water metering, leak detection projects, and weather modification projects.
The DWRe maintains a State of Utah Drought Response Plan and hosts a multi-agency Governor’s Drought Advisory Committee meeting regularly to evaluate drought conditions in the state. Utah’s legislature is incentivizing conservation through a rebate program called Utah Water Savers and the Utah DWRe hosts the Division of Water Resources Conservation Program.
 Read the entire drought chapter
Read the entire drought chapterUtah Drought Website
Producer Response to Drought Policy in the West
Drought Impacts on Livestock
Drought Impacts on National Parks
CASE STUDY

Cache County 1940

Heber 1941
The Dust Bowl Decade from 1933 to 1943 affected approximately 75% of Utah. Agriculture productivity was decreased to almost half of prior years production and the number of farms significantly decreased. In addition to agricultural impacts, water storage supplies rapidly diminished with Utah Lake dropping to 1/3 of its total volume. During the summer of 1934 many communities established outdoor water use restrictions with lawn watering permitted only twice a week.
Utah appealed to the federal government for help and President Roosevelt approved grants totaling $1 million dollars. The money was used to install 276 wells and pipe or line thousands of miles of irrigation ditches.
In 2007 Utah's Division of Water Resources developed Drought in Utah: Learning from the Past; Preparing for the Future. This document emphasizes the need to plan and implement mitigation strategies to ensure a reliable water supply before a drought occurs in order to satisfy future water demand including nine mitigation strategies and recommendations.
